SZG-PCIEX4
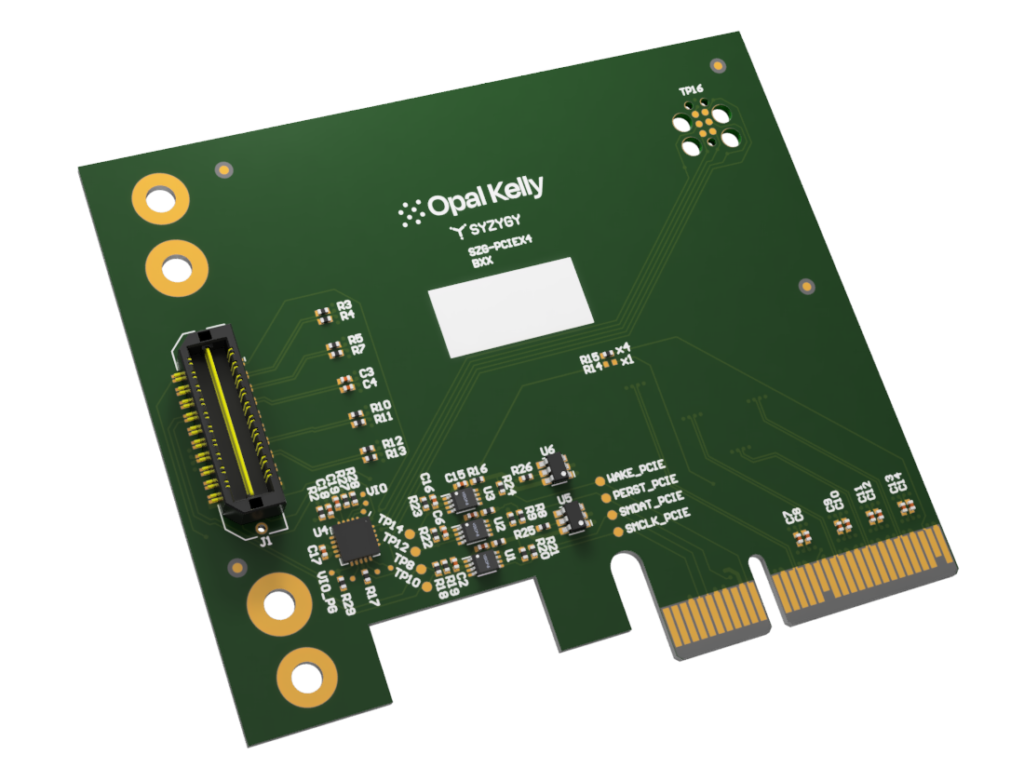
The SZG-PCIEX4 routes the PCIe connector pinout to the SYZYGY Samtec connector. This module is an excellent choice for adding PCIe connectivity to your SYZYGY carrier board. The provided Samtec cable is used to connect the SZG-PCIEX4 to your host PC.
Resources
- Aligni PLM – See the Attachments tab for schematics
- SYZYGY Specification
- SYZYGY GitHub Site – Several projects that could be helpful
- SZG-PCIEX4 Reference Design
- Product Page
Design
A TXR4 SYZYGY ports contain 4 RX/TX lanes connected to a transceiver quad of the FPGA. The SZG-PCIEX4 is a TXR4 (4-lane) peripheral and is compatible with the TXR4 carriers such as the XEM8320, BRK8350, and BRK1900. The PCIe lanes and transceiver quad’s lanes have a same order connection i.e. a 0->0, 1->1, 2->2, 3->3 lane connection. TX lanes are equipt with 0.1-uF coupling capacitors.
Notes and Limitations
Samtec Cable Length
Through internal testing we were able to establish and exercise PCIe Gen 3 x4 Lane links up to 8 feet in cable length. Cable lengths beyond this will either fail to enumerate or train down to lower performance. Performance may vary depending on system hardware and configuration.
Vivado IP Constraint Automation
When using Vivado’s PCIe IPs (XDMA, QDMA, and Integrated Block) you must constrain the PCIe lanes manually to the transceiver bank’s lanes. Within the IP Wizard it is recommended to select Mode “Advanced”, then the “GT Settings” tab will become available. Within the “GT Settings” tab select “true” for “Disable GT Channel LOC Constraint. This will ensure there are no BEL constraint conflicts with these lanes and the manual constraints. Please see the SZG-PCIEX4 Reference Design for a guide on correctly constraining these lanes for your product.
The Vivado PCIe IPs provide XDC files as part of their generated output products which constrain the LOC of the transceiver bank’s lanes to the PCIe lanes as specified in Appendix B of PG213: “PCIe lane 0 is placed in the topmost GT of the top-most GT Quad by default. Subsequent lanes use the next available GTs moving vertically down the device as the lane number increments.” This results in automated LOC constraints for the PCIe’s lanes and transceiver bank’s lanes having the following connections: 0->3, 1->2, 2->1, 3->0. The SZG-PCIeX4 connected to your device through the TXR4 port will have a 0->0, 1->1, 2->2, 3->3 lane connection and is incompatible for automated pin constraints through Xilinx IPs.
Host Powered Enumeration
At the application of power, Opal Kelly’s SmartVIO controller used on Opal Kelly SYZYGY carrier boards enable VIO power supplies later than the required 100ms PCIe standard’s requirement. VIO powers the I/O banks that PCIe PERST ultimately routes to. If the host system requiring enumeration is powering the Opal Kelly SYZYGY carrier board, PERST will not become available under 100ms from the time the host’s power rails become active.
If you’d like the host to power your Opal Kelly SYZYGY carrier board you’ll be required to perform a warm restart of the system to successfully enumerate your PCIe endpoint. A warm restart is a reboot of your host without the removal and reapplication of power.
Alternatively, you can externally power your Opal Kelly SYZYGY carrier board and power on the host after VIO becomes active to achieve a successful enumeration.
Vivado Board File
A companion card board file is available for this SYZYGY peripheral. This companion card board file is only compatible with TXR4 ports on the SYZYGY carrier board’s board file.
Version 1.0 provides the following components:
- PCIe X4 interface
- PERST
How-To Install
Follow the appropriate installation instructions at Vivado Board Files.
Notes
- The SZG-PCIEX4 Companion Card does not automatically constrain the pins for the PCIe X4 Interface to the Xilinx IPs. You must manually constrain these pins through a top level .xdc constraints file or through the GUI. Please see the SZG-PCIEX4 Reference Design for an example of manually constraining these pins on the XEM8320. See “Vivado IP Constraint Automation” under “Notes and Limitations” below for more information regarding the reason for manual constraints.
- PCIe RefClk, which comes from the SZG-PCIEX4 peripheral, needs to be added into your project and connected to your Xilinx PCIe IP. The PCIe RefClk is not currently supported on the board file at this time
SYZYGY Information
Compatibility Table
| COMPATIBILITY PARAMETER | SPECIFICATION |
|---|---|
| Port type | SYZYGY TXR4 (Default) SYZYGY TXR2 (With Modification) |
| Width | Single |
| 5V supply required | No |
| Nominal 5V supply current | N/A |
| Nominal 3.3V supply current | N/A |
| VIO supply voltage | 1.2V-2.5V, 3.3V [1] |
| Nominal VIO supply current | N/A |
| Total number of I/O | 4 |
| Number of differential I/O pairs | 9 |
1 – VIO range may be effected by PCN-20240307
DNA Data
| DNA PARAMETER | DATA |
|---|---|
| Max 5V Load | 0mA |
| Max 3.3V Load | 10mA |
| Max VIO Load | 10mA |
| IS_LVDS | False [2] |
| IS_DOUBLEWIDE | False |
| IS_TXR4 | True |
| VIO Range(s) | [1.2,2.5], [3.3,3.3] |
2 – LVDS flag may be effected by PCN-20240307
Pinout
The source of the following pinout information is the SZG-PCIEX4 schematic. This pinout follows the SYZYGY specification for TXR4 ports.
- Column
PIN NUM (J1)lists the pin number on the SYZYGY specification’s transceiver Samtec connector, this is reference designator J1 in the schematic. - Column
SIGNAL NAMElists the SYZYGY specification’s name for this pin’s connection. - Column
SCHEMATIC NETlists the net name found in the SZG-PCIEX4’s schematic for the connection.
| Pin Num (j1) | Signal name | schematic net |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | RX0p | PCIE_RX0P |
| 7 | RX0n | PCIE_RX0N |
| 6 | TX0p | PCIE_TX0P |
| 8 | TX0n | PCIE_TX0N |
| 9 | RX1p | PCIE_RX1P |
| 11 | RX1n | PCIE_RX1N |
| 10 | TX1p | PCIE_TX1P |
| 12 | TX1n | PCIE_TX1N |
| 13 | REFCLKp | PCIE_REFCLKP |
| 15 | REFCLKn | PCIE_REFCLKN |
| 14 | S0 | PCIE_SMCLK_VIO |
| 16 | S1 | PCIE_SMDAT_VIO |
| 17 | S2 | PCIE_PERST_B_VIO |
| 18 | S3 | PCIE_WAKE_B_VIO |
| 25 | RX3p | PCIE_RX3P |
| 27 | RX3n | PCIE_RX3N |
| 26 | TX3p | PCIE_TX3P |
| 28 | TX3n | PCIE_TX3N |
| 29 | RX2p | PCIE_RX2P |
| 31 | RX2n | PCIE_RX2N |
| 30 | TX2p | PCIE_TX2P |
| 32 | TX2n | PCIE_TX2N |