Encryption Key Storage
The Kintex-7 FPGA supports design security using AES decryption logic and provides two methods for encryption key memory storage. The first is a volatile memory storage supported by an external battery backup supply voltage (Vbatt). The second is a one-time programmable eFUSE register. The XEM7350 design supports both types of key storage with user-modification required for Vbatt support.
For quantity purchases of 50 or more units, please contact Opal Kelly (sales@opalkelly.com) to discuss factory installation of these components.
Volatile Encryption Key Storage (Vbatt)
A small lithium rechargeable battery and three support components can be installed to provide Vbatt to the FPGA when the XEM is unpowered. This will preserve the contents of the FPGA’s volatile key storage so long as Vbatt remains over the threshold specified in the Kintex-7 documentation. Please see the Xilinx 7-Series FPGA’s Configuration (UG470) for more details.
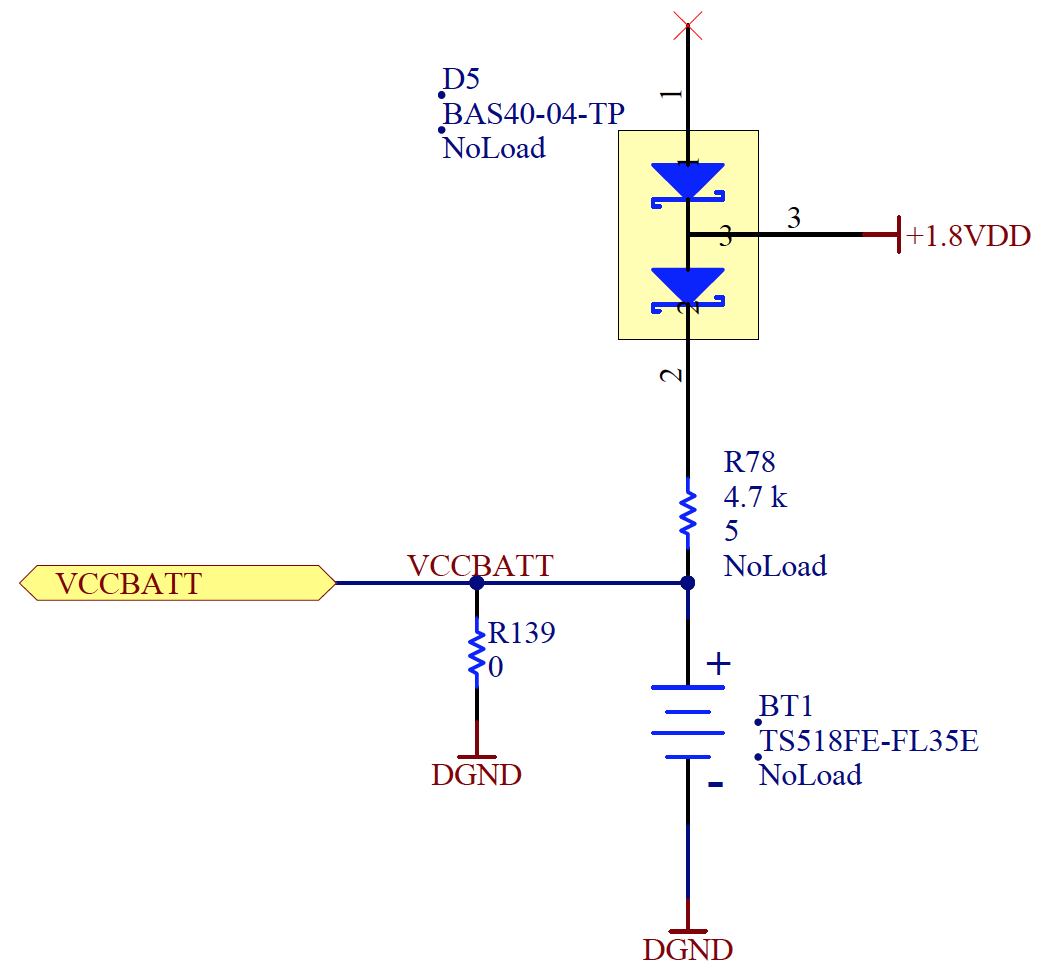
The applicable schematic section and components required to support this functionality are shown below.
| REFDES | MANUFACTURER | MANUFACTURER P/N | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|---|
| BT1 | Seiko Instruments | TS518FE-FL35E | 1.5V, 1.5mAh lithium battery |
| D5 | Micro Commercial | BAS40-04-TP | Schottky Diode, SOT23 |
| R78 | Generic | 4.7 kΩ, 5%, SM-0402 | |
| R139 | Generic | 0 Ω, SM-0402 | Connects Vbatt to DGND(Required if not used) |
Non-Volatile Encryption Key Storage (eFUSE)
Non-volatile storage of the encryption key is also possible by programming the Kintex-7 eFUSE register via JTAG. Please see the Xilinx 7-Series FPGAs Configuration (UG470) for more details.