Example: High Speed DAC/ADC
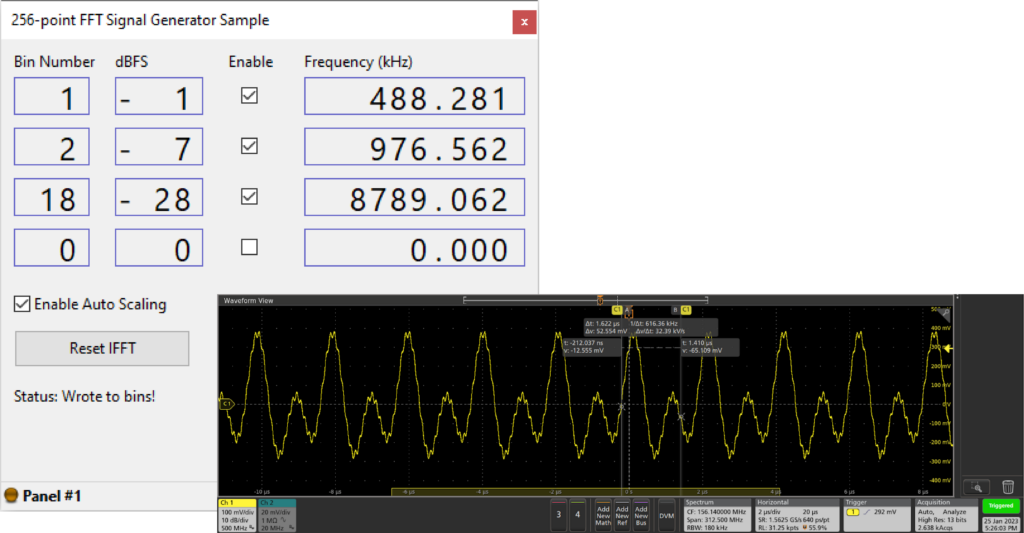
An XFP GUI allows the user to define up to four frequency domain vectors. The FrontPanel Subsystem Vivado IP Core stimulates our HLS Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) core to combine and convert these vectors into a time domain digital output signal. That digital output signal is then converted to analog with our SZG-DAC-AD9116 on the XEM8320-AU25P.
This sample paired with an Opal Kelly FPGA Development or Integration module provides a great starting template for those interested in DSP applications. The sample can be enhanced by additional DSP processing through additional user defined AMD-Xilinx’s HLS cores, or through AMD-Xilinx’s Filter, Modulation, Trig Functions, etc. DSP IP Cores.
Artix-7 and Legacy ADC and DAC Example Support Information
We currently have simpler ADC and DAC example designs available on our open source Github that target the XEM7320 and the XEM8320. Note, these are no longer supported or maintained.
The ADC design is a simple scope that uses Python to display the signals from the ADC. More information is available in the READMEs for the desired XEM module.
The DAC design features AM/FM modulation and can pipe audio into the design to modulate it over a carrier wave with the requested parameters. You can learn more about it on our blog, here.
Resources
- GitHub: Opal Kelly’s HLS Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Core
A synthesizable and scalable pipelined fixed-point Decimation-in-Frequency FFT and IFFT FPGA library for use with AMD-Xilinx’s High Level Synthesis (HLS). - GitHub: FFT Signal Generator Sample
A complete sample using HLS FFT and IFFT cores. This sample targets the XEM8320, SZG-DAC-AD9116, and SZG-ADC-LTC226x.
Learning Objectives
Users will be able to:
- Create IPI Block Designer projects utilizing the FrontPanel Subsystem Vivado IP Core.
- Use an XFP GUI with FrontPanel Scripting for GUI control of gateware.
- Get introduced to a workflow that incorporates FrontPanel and AMD-Xilinx’s High Level Synthesis (HLS) components.
- Use the FrontPanel Alloy GUI to set frequency bins and view the frequency domain of measured signals.
Getting Started
The end result of this tutorial is to use our prebuilt bitfile in-hardware to produce the following three-tone wave and capture it on an oscilloscope:
Requirements
- Latest FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y release files:
–FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.bit
–FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.lua
–FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.xfp - FrontPanel 5.2.12 or later
- XEM8320-AU25P
- SZG-DAC-AD9116 on Port A
- SZG-ADC-LTC226x on Port B (if using FrontPanel Alloy GUI)
- Oscilloscope (if not using FrontPanel Alloy GUI)
Note: For best results, use an oscilloscope with 200 MHz bandwidth to best represent the SZG-DAC-AD9116’s full Nyquist bandwidth of 62.5MHz.
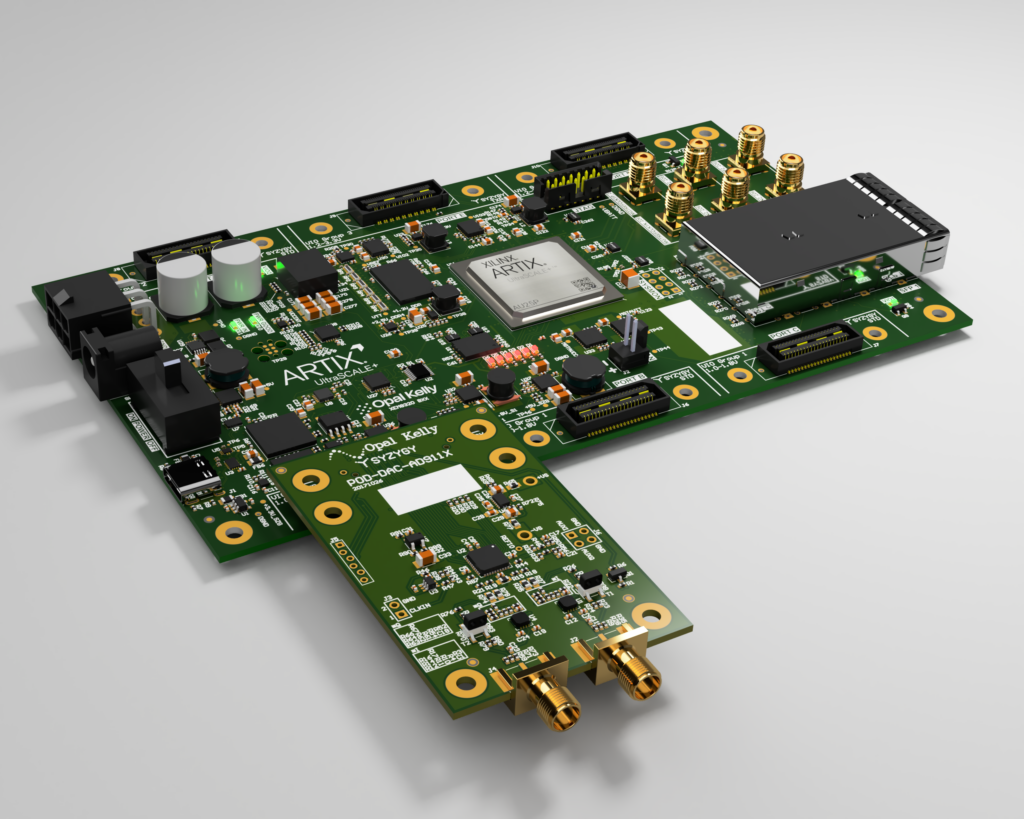
Running the Sample
Hardware Setup
- Connect a SZG-DAC-AD9116 to port A on the XEM8320-AU25P.
- Connect a SZG-ADC-LTC226x to port B on the XEM8320-AU25P (if using FrontPanel Alloy GUI).
- Power on the XEM8320-AU25P using a 12-volt supply.
- Connect the XEM8320-AU25P to a PC using a USB-C cable.
Oscilloscope Setup
- Connect an oscilloscope probe to either SZG-DAC-AD9116 output’s center pin, and ground the signal on the outer SMA connector, if using a standard probe.
- Set the oscilloscope to center 0 volts, with a vertical range of +/- ~1 volt.
FrontPanel Application Setup
- Open FrontPanel 5.2.12 or later (6.0.0 or later if using the Alloy GUI).
- Click the Download FPGA Configuration button and select
FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.bit. - Click the Load FrontPanel Profile button and select
FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.xfp.
Note:FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.luaneeds to be in the same directory asFFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y.xfp.
Sample Application Setup
- Click Reset IFFT.
- Enable Auto Scaling.
- Enable bins 1, 2, and 3. Leave bin 4 disabled.
- Set bin 1 to bin number 1, bin 2 to bin number 2, and bin 3 to bin number 18.
- Use your mouse’s scroll wheel to set their corresponding dBFS values to -1, -7, and -28.
- There should now be a three-tone sine wave displaying on the oscilloscope, as shown below.
How-To Setup the Project
We provide various build scripts for instructing Vitis HLS to build our FFT core, creating the Vivado project, configuring the required IP Cores, and constructing the IPI Block Design Project. The end result of this How-To is the construction of the following Vivado IPI Block Design project:
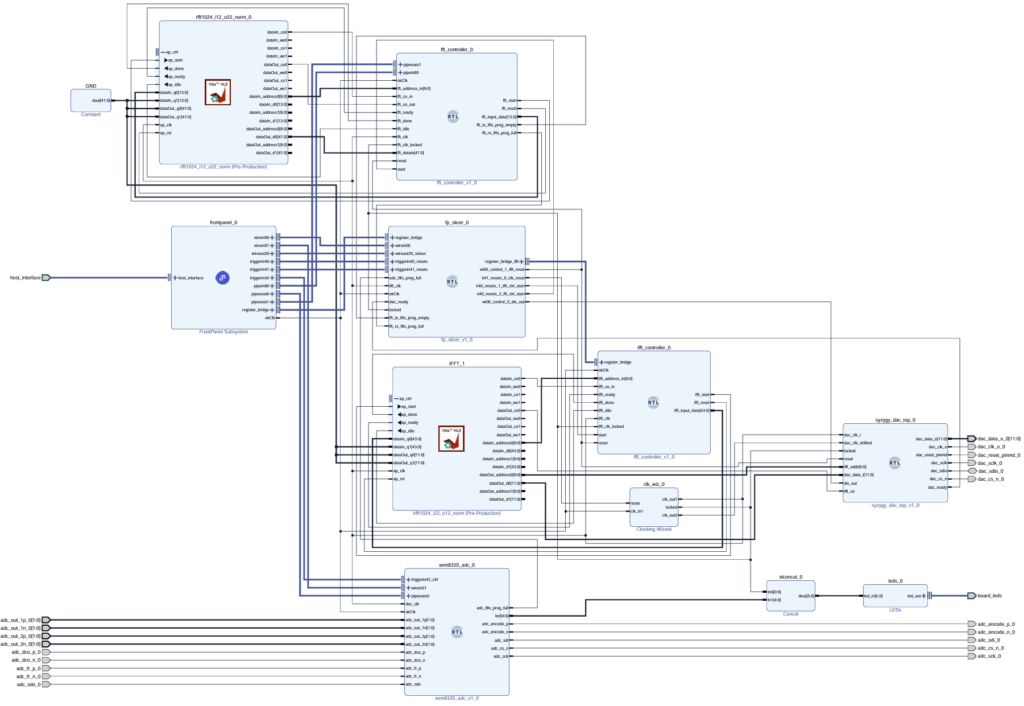
This design requires the following to build:
- Vitis HLS
Notice: Our supported version is v2023.2. Versions outside of this are not guaranteed to be maintained. - Vivado
Notice: Our supported version is v2023.2. Versions outside of this are not guaranteed to be maintained. - Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution v1.0.2 or later
- XEM8320-AU25P Board file v1.2 or later
- Latest FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y release Source Code (zip or tar.gz)
Windows
- Follow How-To Install for the XEM8320-AU25P’s Board file v1.2 or later.
- Follow Add IP Cores’ Distribution to Vivado for Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution v1.0.2 or later. The location you installed this Distribution to will be used in step 6.
- Extract the sample’s release zip/tar.gz.
- Open a command prompt and
cdto the directory containing the sample’sBuildfolder.cd C:/pathToDownload/design-resources-FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y/ExampleProjects/FFT_Sample/Build
Note: PowerShell won’t work, Command Prompt must be used. - Run the
settings64.batfile in the Vitis HLS and Vivado installation directories.path/to/vitis/2022.1/settings64.batpath/to/vivado/2022.1/settings64.bat - Run the .bat file with the path to the Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution as an argument.
windows_create_project.bat C:/pathToDownload/FrontPanel-Vivado-IP-Dist-vX.Y.Z
Linux
- Follow How-To Install for the XEM8320-AU25P’s Board file v1.2 or later.
- Follow Add IP Cores’ Distribution to Vivado for Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution v1.0.2 or later. The location you installed this Distribution to will be used in step 6.
- Extract the sample’s release zip/tar.gz.
- Open a terminal window and
cdto the directory containing the sample’sBuildfolder.cd pathToDownload/design-resources-FFTSignalGenerator-vX.Y/ExampleProjects/FFT_Sample/Build - Run the
settings64.shfiles in the Vitis HLS and Vivado installation directories.source path/to/vitis/2022.1/settings64.shsource path/to/vivado/2022.1/settings64.sh - Run the .sh file with the path to the Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution as an argument.
linux_create_project.sh pathToDownload/FrontPanel-Vivado-IP-Dist-vX.Y.Z
How-To Run the Behavioral Simulation
We utilize the Behavioral Simulation features of the FrontPanel Subsystem Vivado IP Core to provide a simulation of the Signal Generator. The end result of this How-To is the creation of a simulation waveform for a two-tone wave:
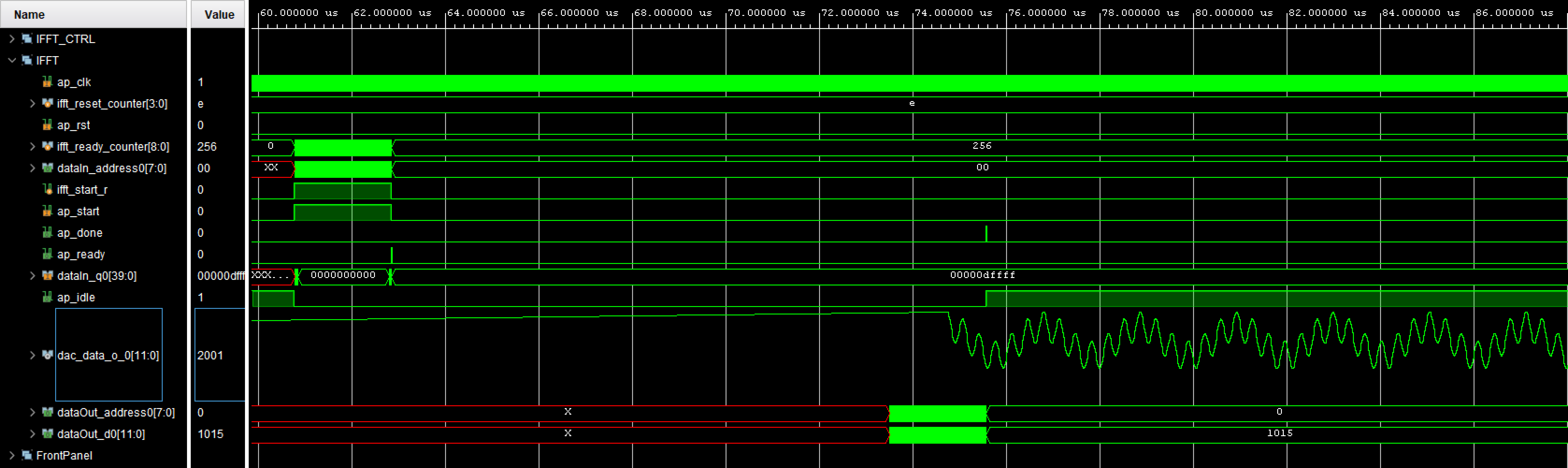
- Follow How-To Setup the Project
- In Vivado, launch Flow>Run Simulation>Run Behavioral Simulation
- Launch Run>Run All
How-To Generate the Bitfile
- Follow How-To Setup the Project
- In Vivado, launch Flow>Generate Bitfile
Gateware Architecture Reference
Below we define terms and three important data flow stages for this sample:
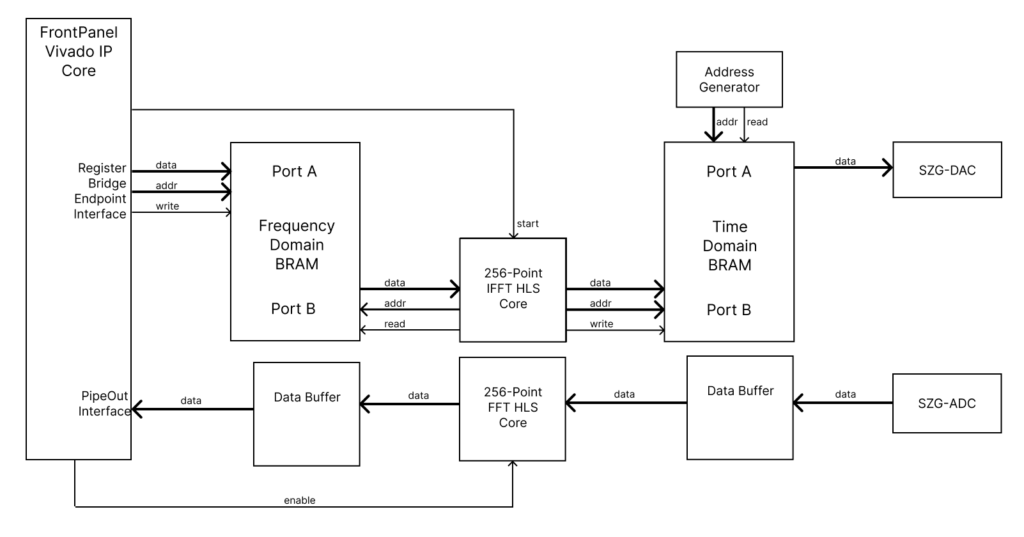
- Frequency Domain BRAM – Contains the 256 frequency domain vectors the FFT computes with.
- IFFT Start – The XFP GUI with FrontPanel Scripting communicates with the FrontPanel Subsystem Vivado IP Core generated FrontPanel HDL endpoints to store the Vector Set into the Frequency Domain BRAM. A custom RTL Slicer is used to distribute control signals throughout the design.
- Enable – Enables the FFT core to calculate the SZG-ADC input.
Software
XFP GUI Reference
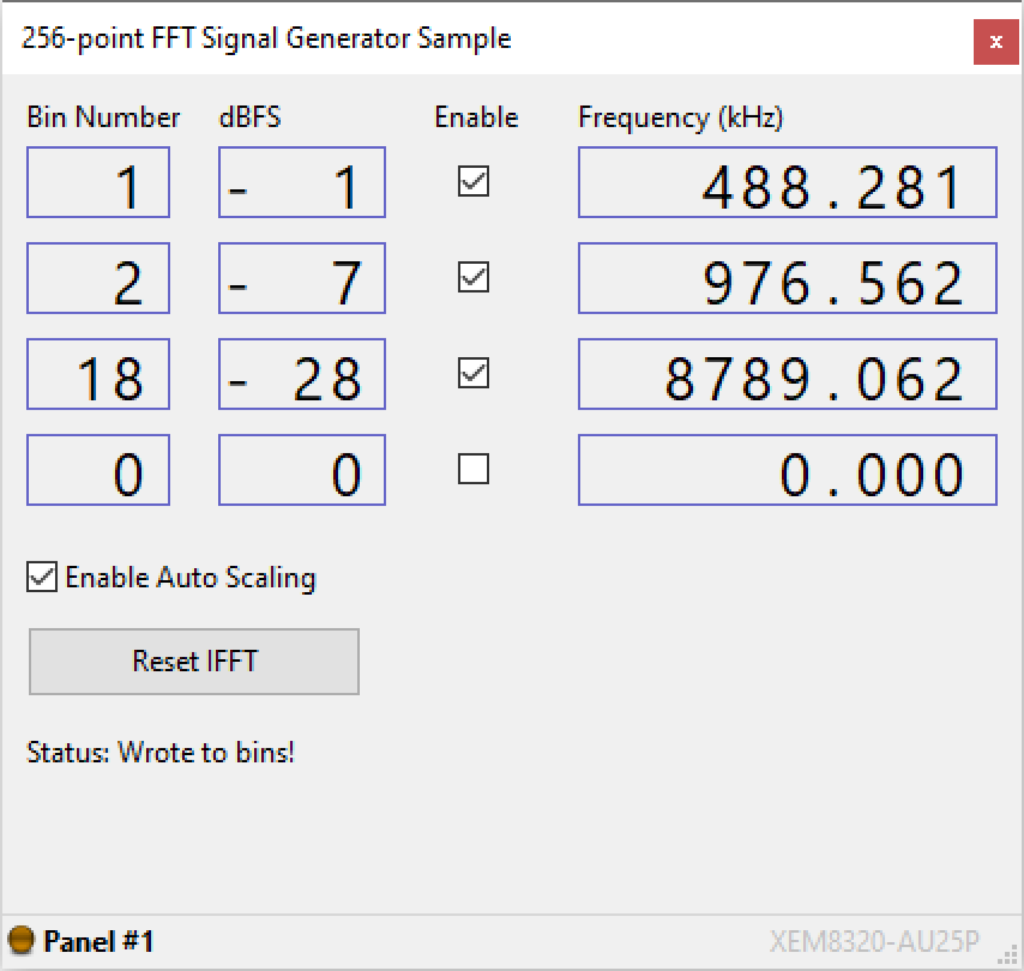
The user interface shown above has the following components to control the behavior of the FFT signal generator:
- Bin Number – This selects a frequency bin number in the FFT to activate, from 0 to 127.
- dBFS – DeciBel Full Scale. 0 = full power, 120 = nearly off.
Note: You must use your scroll wheel to input into this entry - Enable – If unchecked, disables the bin. Also discludes the dBFS value from any Auto Scaling calculations.
- Frequency (kHz) – The frequency of the specified Bin Number.
- Enable Auto Scaling – If enabled, will prevent the sum of all the bin values (calculated from dBFS) from going over the maximum. This will prevent clipping. For example, if two bins were enabled with a dBFS of zero, the Lua script will halve the components to the selected bins and the output signal from the SZG-DAC will not be clipping.
- Reset IFFT – Resets the design.
FrontPanel Alloy Application
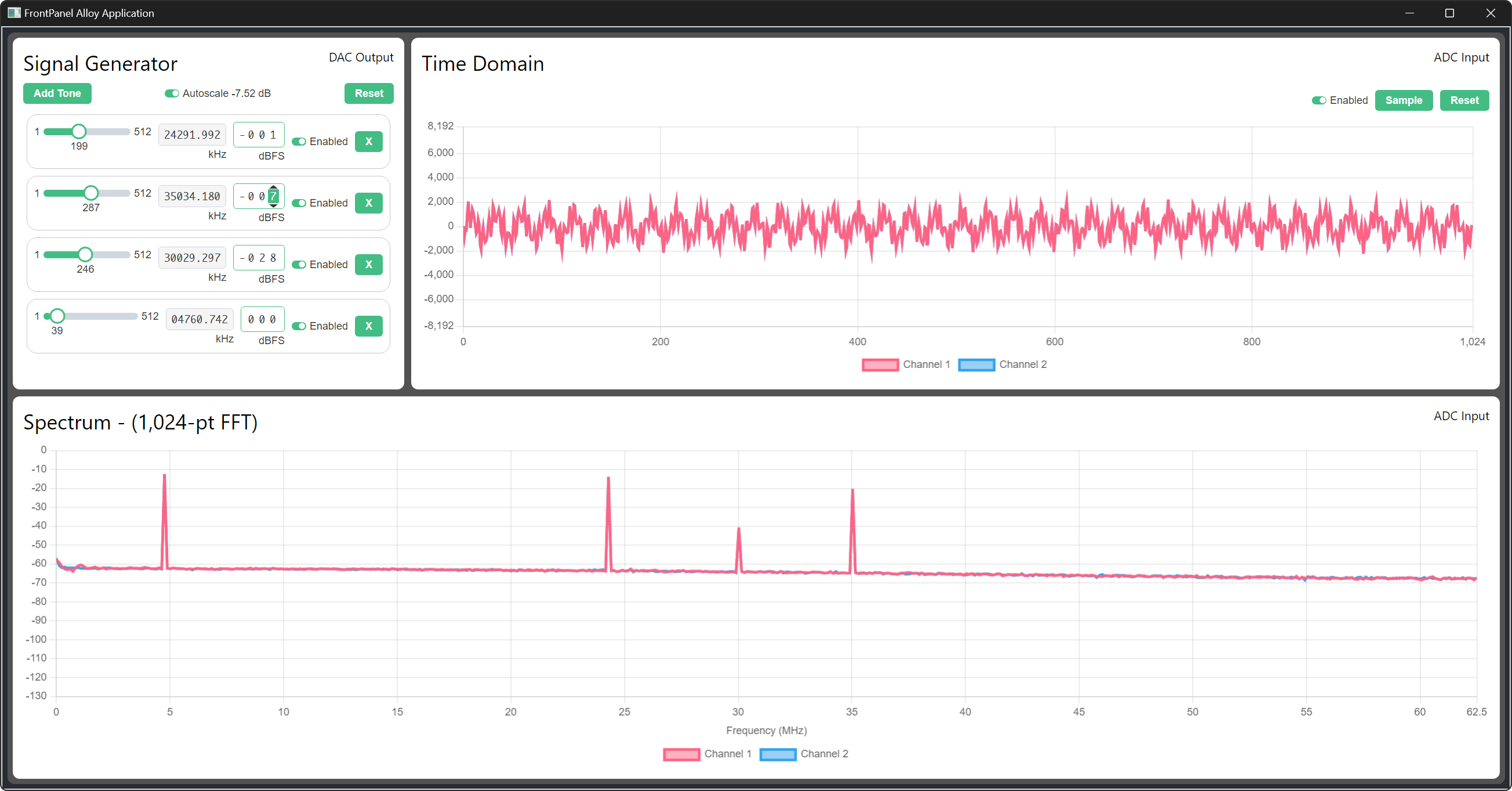
Limitations
A limitation of the provided XFP and Lua script is the lack of the ability to set the phase of the frequency domain vectors. This involves incorporating the complex component of the frequency bins. In gateware, the functionality to do this is present, but is not implemented in the XFP and Lua script.
Release Notes
Our supported releases for the FFT Signal Generator sample are located on GitHub at:
opalkelly-opensource/design-resources Releases
High Speed DAC/ADC 1.1
- Renamed design
- Added ADC + IFFT functionality
- FrontPanel Alloy GUI functionality
FFT Signal Generator 1.0
- Initial Creation
- Bitfile generated using the following tool versions:
Vivado v2022.1
Vitis HLS v2022.1
Vivado IP Cores’ Distribution v1.0.2
XEM8320-AU25P Board file v1.2