Powering the XEM7010
The XEM7010 requires a clean, filtered, DC supply within the range of 4.5 V to 5.5 V. This supply must be delivered through the DC power connector or the expansion connector MC1.
The XEM7010 power distribution system includes several supplies designed to provide suitable, efficient power for several systems and modules. A schematic diagram of the system follows, with input (+VDC) shown to the left and accessible supply rails shown to the right.
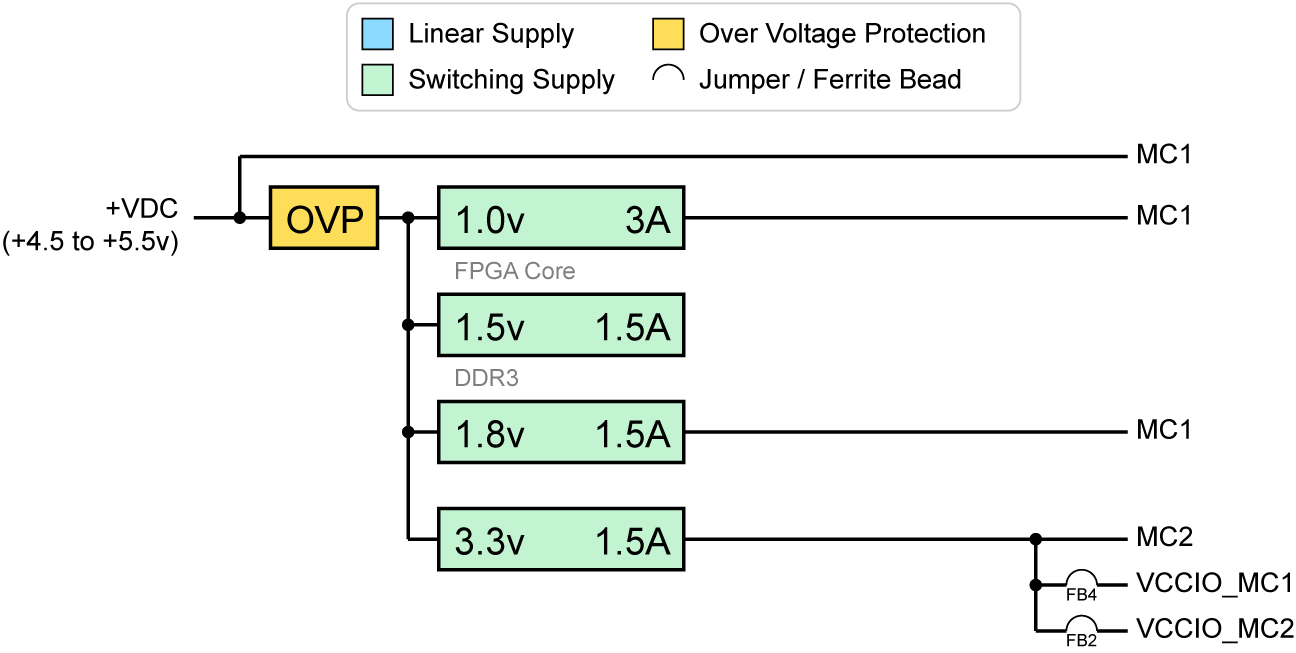
Power Supply
The XEM7010 is designed to be operated from a single 5-volt power source supplied through the DC power jack on the device. This provides power for the several high-efficiency switching regulators on-board to provide multiple DC voltages for various components on the device as well as three adjustable supplies for the peripheral.
DC Power Connector
The DC power connector on the XEM7010 is part number PJ-102AH from CUI, Inc. It is a standard “canon-style” 2.1mm / 5.5mm jack. The outer ring is connected to DGND. The center pin is connected to +VDC.
Powering via USB
The XEM7010 has been designed to accept power (+5VDC only) via the USB connector with a small modification. To power from USB, you will need to install a 0 Ω resistor (0603 dimension) at location R46, located on the reverse side of the PCB under the power connector. This will connect the +5VUSB from the USB connector to the +5VDC on the XEM7010.
With this resistor in place, you should not apply +5VDC to the external power connector.
Over Voltage Protection
An electronic fuse on the +VDC input protects the module from overvoltage, undervoltage, and thermal overload conditions. During any one of these conditions, the fuse enters a fault state. In the fault state, the FAULT LED illimunates red and all down-stream power supplies on the module are disabled.
The table below indicates the overvoltage and undervoltage thresholds. The fault state clears automatically when the +VDC input voltage is within the specified range.
| CONDITION | RISING THRESHOLD | FALLING THRESHOLD |
|---|---|---|
| Overvoltage | 5.56 V | 5.12 V |
| Undervoltage | 3.97 V | 3.69 V |
Current Overload
The fuse has an overcurrent limit of approximately 5 A. A current overload condition does not cause the fuse to enter the fault state. Instead, the fuse enters a current limit mode, dissipating power internally to keep the output current at or below the 5 A limit. If the current overload condition continues and the thermal shutdown threshold is reached, the fuse enters the fault state. An automatic retry cycle will clear the fault state when the thermal overload condition no longer exists.
Reverse Voltage
The fuse protects against a reverse voltage/current condition, but the FAULT LED does not illuminate during this condition.
Power Budget
The table below can help you determine your power budget for each supply rail on the XEM7010. All values are highly dependent on the application, speed, usage, and so on. Entries we have made are based on typical values presented in component datasheets or approximations based on Xilinx power estimator results. Shaded boxes represent unconnected rails to a particular component. Empty boxes represent data that the user must provide based on power estimates.
The user may also need to adjust parameters we have already estimated (such as FPGA Vcco values) where appropriate. All values are shown in milliwatts (mW).
| COMPONENT(S) | 1.0V | 1.5V | 1.8V | 3.3V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 MHz | 100 | |||
| USB | 280 | |||
| DDR3 | 285 | |||
| FPGA Vccint, Vccbram | ||||
| FPGA Vccaux | 500 | |||
| FPGA Vcco34 (DDR3), est. | 170 | |||
| FPGA Vcco14 (USB), est. | 110 | |||
| FPGA Vcco | ||||
| Total (mW) | ||||
| Available (mW) | 3,000 | 2,250 | 2,700 | 4,950 |
Example XEM7010-A200 FPGA Power Consumption
Xilinx Power Estimator version 2015.3 was used to compute the following power estimates for the Vccint supply. These are simply estimates; your design requirements may vary considerably. The numbers below indicate approximately 80% utilization.
| COMPONENT | PARAMETERS | VCCINT | VCCAUX |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clock | 150 MHz GCLK, 220,000 fanout | 570 mW | |
| Logic (DFF) | 150 MHz, 220,000 DFFs | 550 mW | |
| Logic (LUT) | 150 MHz, 100,000 | 550 mW | |
| BRAM | 36-bit, 300 @ 150 MHz | 450 mW | |
| DSP | 150 MHz, 630 slices | 300 mW | |
| Misc. | DCM, PLL, etc. | 10 mW | 500 mW |
| Total | 2,430 mW | 500 mW | |
| Available | 3,000 mW | 2,700 mW |
FPGA Power-On Sequencing with External VCCO
The Artix-7 family of devices has the following recommended power supply startup sequence:
- VCCINT/VCCBRAM
- VCCAUX
- VCCO
This sequence achieves minimum current draw and ensures I/O are tristated at power-on. For more information see the “Power-On/Off Power Supply Sequencing” section in the Artix-7 FPGA Data Sheet (DS181).
To meet this sequencing recommendation when applying external VCCO power supplies, the external system should monitor the XEM7010 +1.8VDD supply on mezzanine connector MC1, pin 7. This on-board voltage rail powers the FPGA VCCAUX pins directly. After the +1.8VDD rail is within regulation (within ±10%, for example), the external system may apply VCCO to the module.